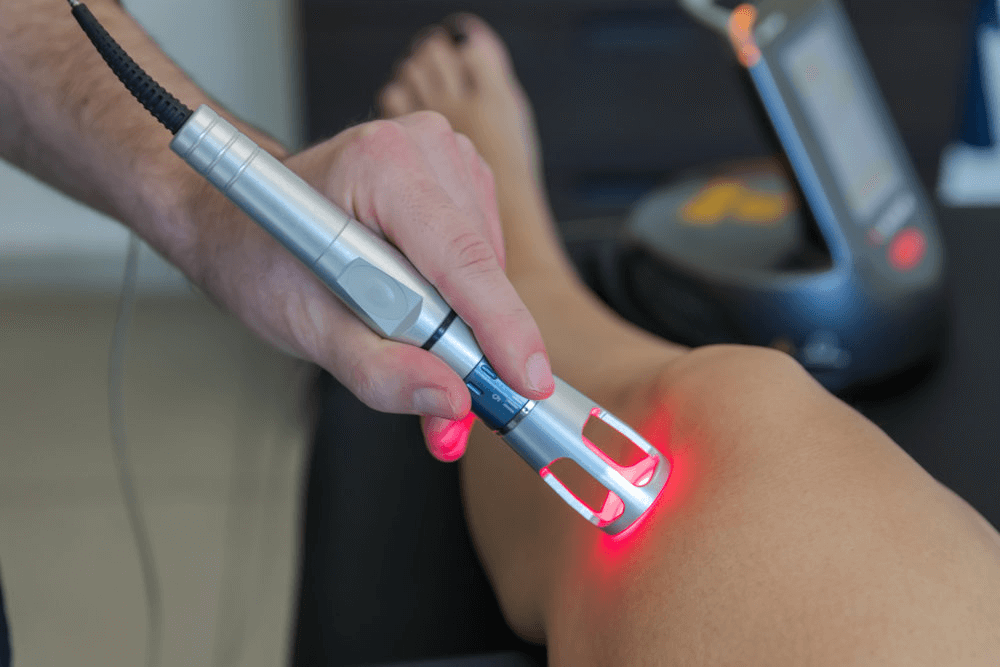
Cold laser therapy or Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT) is not a newborn treatment. For now, there are more than four decades of clinical use for treating many conditions. Patients like it for cold laser therapy because it is non-invasive and brings no pain.
Photobiostimultion is another term for cold laser therapy. has approved it for treating pain, inflammation, soft tissue injuries, degenerative joint disorders, back and neck pain, etc. Cold laser therapy is also effective in improving skin conditions and reducing hair loss.
In this article, we look at evidence-based applications of cold laser therapy and go through the myth and facts about the treatment.
How does cold laser therapy work?
Cold laser therapy does not actually freeze tissues. Compared to infrared light, the light from photobiomodulation devices does not cause any thermal effect in cells. During the procedure, you will feel nothing. For this reason, it is called “cold laser therapy”.
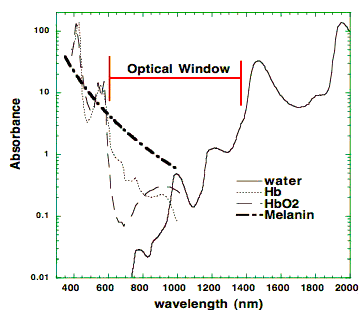
All devices emit light in the range from (~600 nm) to near-infrared (~950 nm). This spectrum is called an “optical window”. In this range, light can penetrate through the skin and is little absorbed by water, melanin, or hemoglobin in the blood.
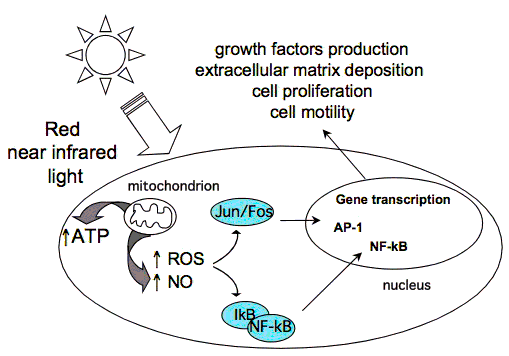
While laser light penetrates into the cell, it induces the production of extra energy in mitochondria. These organelles produce ATP which acts as the main power source for all processes in cells. As the energy level increases, it elevates metabolism in it.
In addition to high energy, red and near-infrared light increases the production of nitric oxide (NO) and modulates reactive oxygen species (ROS). The first one is a powerful vasodilation factor and signaling molecule. The latter regulates many signaling pathways in cells including inflammatory response.
As a result of described events, cells start to work more actively. They divide faster and produce more proteins, collagen, etc. Moreover, cells avoid death and restore their normal functioning.
- Cell growth. Low-level laser therapy (LLLT) stimulates the division of the cells and their growth.
- Wound healing. Cold laser therapy stimulates collagen production in fibroblasts which cause faster healing.
- Increased metabolic activity. As red and near-infrared light increases the energy level of the cells.
- Alleviation of pain or inflammation
- Increased vascular activity and circulation. Cold laser therapy enhances the formation of new blood vessels in the treated area.
Stimulation of nerves recovery. After the injury limbs can feel numb, while cold laser therapy will stimulate reconnection of the nerves.
What can you treat with low-level laser therapy?
Pain and injuries
Cold lasers are FDA-cleared technology for treating acute and chronic pain. It has a strong scientific base for relieving pain and treating musculoskeletal disorders, which include arthritis, osteoarthritis, back or neck pain, epicondylitis (tennis elbow), carpal tunnel syndrome, etc.
One systematic meta-analysis [2] reviewed 21 head-to-head compressions between the LLLT group and the control group with a total number of participants of 1462. 17 studies showed significant improvement in the decrease of pain among treated patients. That is considered a good evidence rate.
Skin issues
Cold laser therapy is effective for treating wrinkles, acne, acne scars, hypertrophic scars, and healing burns. It reduces skin UV damage and shed signs of aging. For example, 90 % of patients showed a significant reduction in wrinkles depth and surface roughness [3].
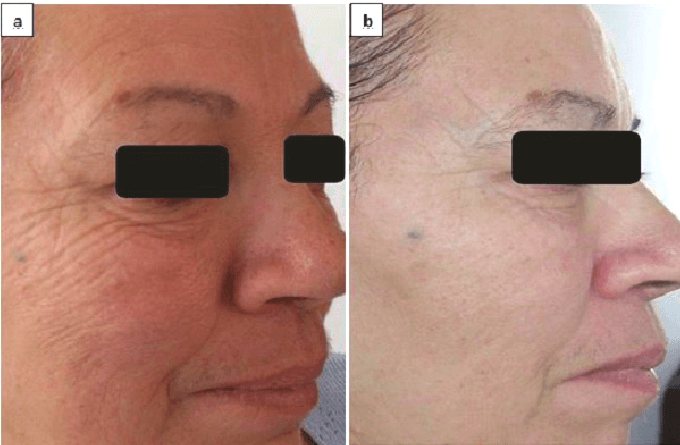
Cold laser therapy also prolongs symptom-free periods for patients with the recurrent herpes virus. Patients who received daily irradiation for 2 weeks on average showed 37.5 weeks of recurrent-free period, while in the control group this period was only 3 weeks [4].
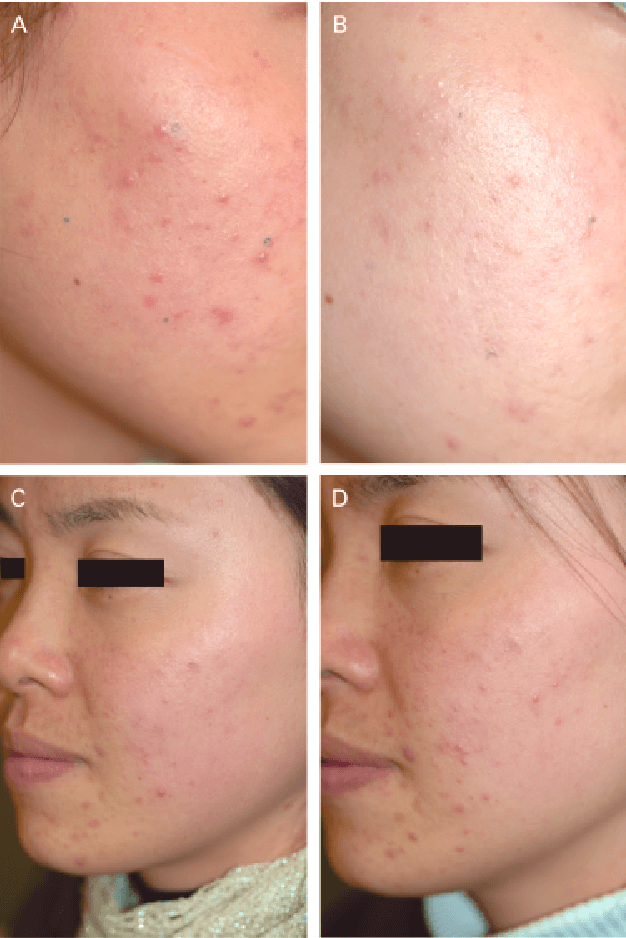
LLLT is successfully used for treating acne. The study [5], which involved 28 patients showed that treatment with red light decreased the total number of lesions by almost 5 times compared to the control.
Another common use is to treat pigmentation issues. For example, one study [7] showed that cold laser therapy increases repigmentation by >50% for patients with segmental-type vitiligo.
Cold light therapy is also helpful with psoriasis, edema, dermatitis, rashes, and burns [8].
Wound healing
Cold laser therapy promotes wound healing by stimulating cells to excrete cytokines, chemokines, and other active signaling molecules. It increases the mobility of immune cells in the injured area and the production of new collagen. As a result, the period of healing gets shorter.
The results of research on wound healing are a little conflicting. While one study [9] shows that the group with low-level laser therapy (LLLT) showed greater wound contractions. Another one states no significant difference between groups [10].
To prove the efficiency of cold laser therapy more well-designed research is needed. Cold laser therapy has the potential to help with healing injuries for people with diabetes [11]. So with more research LLLT can be implemented in common medical practice to help thousands of people.
Hair loss
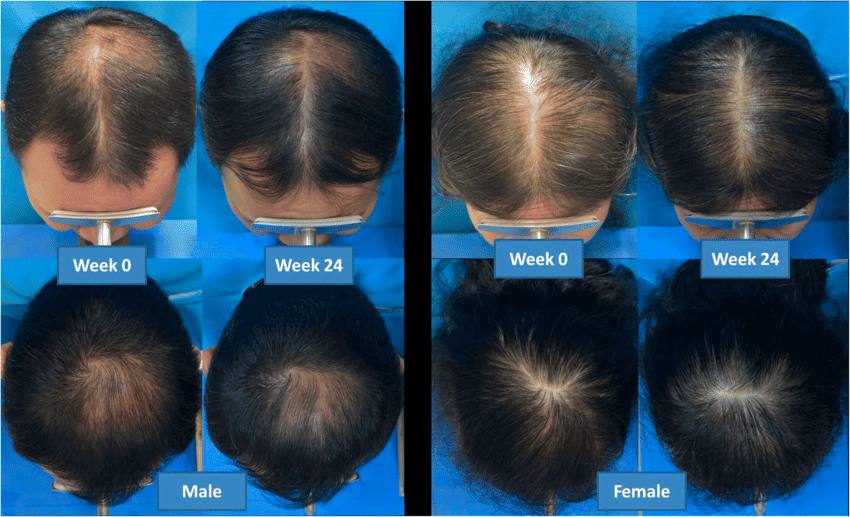
Hair loss or alopecia affected 50% of males over 40 and 75% of females over 65. Cold laser therapy shifts thair follicles to the active proliferation phase. There is over a decade of research that proves the efficiency of biomodulation in treating hair loss.
A systematic review [12] of 10 controlled clinical studies demonstrated that LLLT positively affected hair counts, hair growth, and hair coverage in treatment groups. All studies showed no or a few side effects. They include skin sensitivity, acne, and pruritis which are resolved within 2 weeks.
For example, one study [13] demonstrates an increase of 51% in hair counts after 24 weeks of treatment compared to the sham group.
Find the best laser for the therapy
Laser classes / Power
Depending on the laser power they are divided into 4 classes from 1 to 4.
- Class 1 and 2
These lasers you can get over-the-counter. They are suitable for treating humans and animals. The maximum power reaches 5mW. Some typical examples are laser pointers, barcode readers, and LEDs devices.
They are safe for the eyes and cheaper compared to devices in other classes. However, their power is only enough to treat cutaneous issues. To deliver enough energy to the tissues you might use them for long periods several times per day.
- Class 3
Class 3 lasers have power up to 500mW. They can cause eye damage, so you need to wear protective goggles for procedures.
This class is divided into categories 3a and 3b. 3b lasers are the most studied and have a proven therapeutic effect. To buy these devices you need to have recommendations from the health care providers.
- Class 4
Lasers from Class 4 are more effective in delivering a high amount of energy to deeply-located tissues. They are identical to the Class 3 in a therapeutic effect, however, are less safe. It can damage the eyes and cause tissue burning.
The same as with Class 3, you can buy these devices only with a recommendation letter from the doctor.
Wavelength
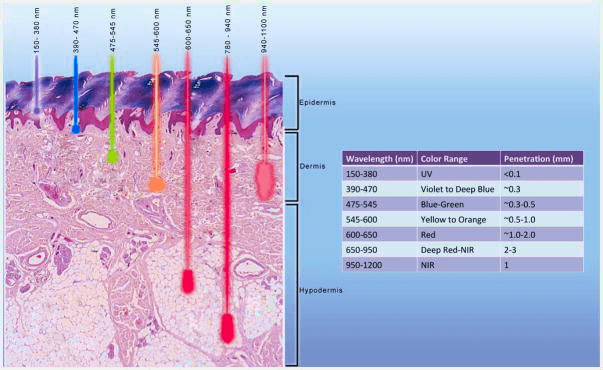
Most lasers deliver light with wavelengths between 600 and 950 nm. This range is called “optical window”, as these waves are mostly absorbed by cells, not water or hemoglobin in the blood. It explains the therapeutic effect of the laser.
Depending on the light wavelength you can treat different conditions.
- The range of 600-700 nm is suitable for treating superficial tissue, for example, skin issues or hair loss.
- Waves of the length between 780 and 950 nm have more energy, so they can penetrate deeper into tissues.
- 700-780 nm range has shown no pronounced therapeutic effect yet
- A wavelength of 900 to 1050 nm is used for the super pulsed lasers (~910 nm) or for class 4 lasers (~950) for treating pain and inflammation. The energy from the waves is mostly converted into heat, so it creates fewer photobiomodulation effects.
Pulsing feature
There are two options available on the market: pulsing lasers and continuous waves. However, some more pricey devices propose both options for one machine.
Pulsing lasers emit high-level energy during pulsing. These devices can deliver energy equal to Class 3 lasers, however, they are considered safe. Compared to constant lasers it takes more time to deliver enough amount of energy to the tissue. They are more suitable for long-term treatment.
Constantly lasers give a high dosage quickly and are good for getting immediate results.
Laser or LED
You might see machines either with a laser or LED inside, which is still called “cold laser therapy”. As well as lasers, LEDs are shown to reveal pain and inflammation.
Both laser and LED can be built to emit light in the red and near-infrared spectrum, however, there is a significant difference between them.
- Focus. Laser light scatters less while entering the tissue compared to LEDs. It helps to go deeper in the tissue and focus treatment in one area.
- Range of wavelength. While laser emits light only of one defined length (~1nm), LED produces a small band of wavelengths (~20 nm wide). This can be an issue while the goal is to specifically target one tissue.
- Depth of treatment. Lasers are more suitable for treating deeper or more widespread conditions (chronic pain, arthrosis, or neuropathy). LEDs are better to treat superficial issues, for example, would healing or hair loss. They are also too weak to reach deep tissues.
Myths and facts about cold laser therapy
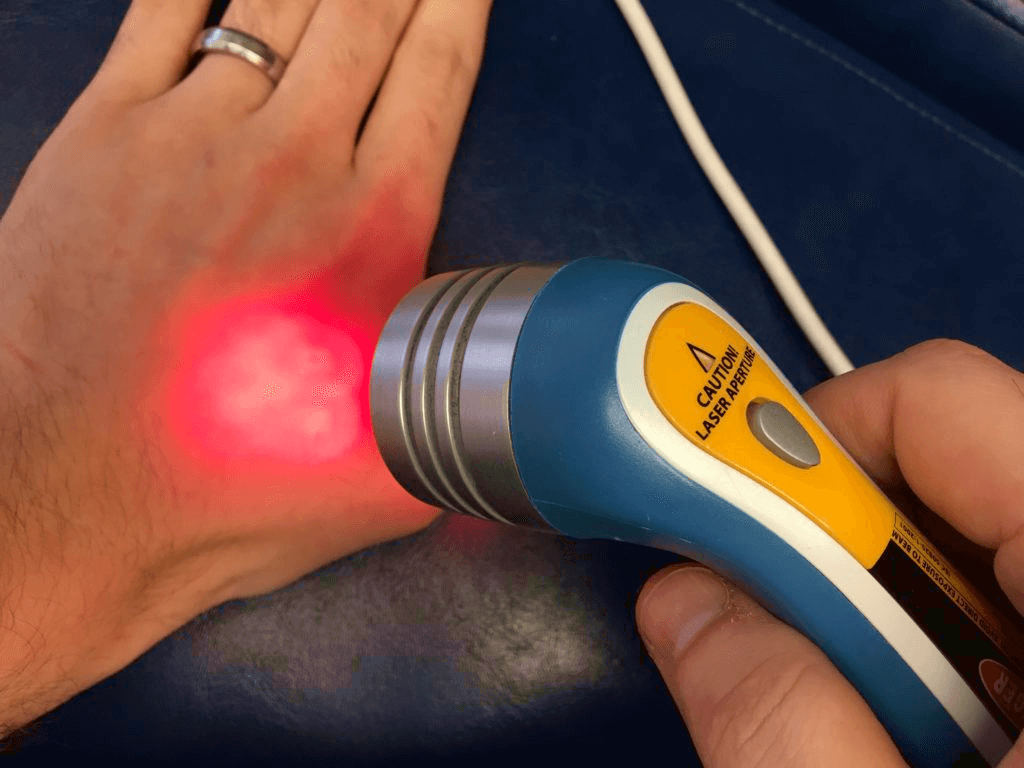

Myth 1: Cold lasers can’t burn the skin
It depends on the class of laser. Some mid-range or high-end lasers in Class 3b and lasers from Class 4 can burn the skin if held in one place for a longer time than prescribed.
Myth 2: If I use a cold laser as often as I can, I will get better results
Not really. For at-home devices, you should follow the instructions for the particular machine. Some recommend having a procedure every other day, while for others it is 2-3 times every day. For in-office, you will discuss the duration and frequency individually depending on your aim and light source.
Overuse of the device can result in pigmentation changes, redness, increase in redness, and even burns.
Myth 3: LED light is not effective for cold laser therapy
LED light can be used in devices for cold laser therapy. However, they are only effective in treating superficial issues, as the LED light doesn’t go deep into the tissue.
Myth 4: At-home devices are neither safe nor effective
Most home devices are safe to use. However compared to professional devices they deliver less energy to tissues, so the result can be less noticeable. Moreover, many at-home devices lack research on efficiency. It’s better to analyze reviews wisely, to select the best model.
Pros and Cons of cold laser therapy
Pros
- Painless. During the treatment, you will feel nothing. As the laser doesn’t heat tissues, vibrate, or emit any sounds it causes no harm to cells.
- Non-invasive. Cold laser therapy is an effective fully non-invasive treatment for pain, arthritis, soft tissue injuries, hair loss, etc
- Versatility. Cold laser therapy devices can be used for treating many conditions in both humans and animals.
- Non-toxic. Low-level laser therapy (LLLT) doesn’t use any toxic chemicals or drugs during treatment.
- Easy-to-apply. The procedure of cold laser therapy is very straightforward. You need to apply the light directly to the treatment area with recommended intensity level and time.
- Safe. Most cold lasers (except ones from Class 4) have no thermal effect and can cause damage to the cells. Starting from Class 3 you need to wear protective goggles to avoid eye damage.
Cons
- Requires many sessions. While you can see primary improvement starting from the first use. For getting constant results you need to follow the treatment schedule.
- Controversial therapy. While cold laser therapy is popular among chiropractors, acupuncturists, and physical therapists, many practitioners doubt in is efficiency. More precise studies are needed to fully approve photobiomodulation for common medical practice.
What are the side effects of cold laser therapy?
Luckily cold laser therapy doesn’t have any major side effects if used according to instruction.
❗ Warnings before using
- Always wear protective goggles to prevent eye damage.
- Strictly follow the user manual, including settings for intensity, time, and wavelength. If you are not about something it’s better to ask a provider for consulting.
- Concerning the powerful biostimulation effect irradiation of the neck region should be done with caution as it can cause hyperthyroidism.
- People with epilepsy should also consult with a doctor before using pulsing devices.
Contraindications of low-level laser therapy
There are a few conditions that restrict the use of cold laser therapy.
Pregnant women should avoid low laser therapy on the abdomen as there is no research on the fetus’s safety.
Cancer or potentially cancerous lesions are also contraindications for the treatment. Photobiomodulation stimulates cell growth and division. However, there are some studies on the beneficial impact of cold laser therapy on treating cancer, you should consider it only with a doctor’s recommendation.
People with any blood disease including anemia, hemophilia, or blood clots should also restain from low-power laser therapy (LPLT) or consult with a professional if symptoms are mild.
Moreover, you should avoid using laser therapy in areas near pacemakers, metallic implants, or defibrillators.
At-home devices vs. professional machines
| At-home devices | At-office session | |
| Price | Starting from $150 to $2000+ for powerful and FDA-clarified devices. | One session costs between $50 and $200. |
| Effectiveness | To be effective these devices require prolonged sessions and a high frequency of treatment. Usually, they have less evidence for its efficiency. | Most FDA-approved devices are machines for professional use. |
| Conditions to treat | Chronic disease that requires a long treatment period or minor issues that can be treated without a device with much power. | If you have acute conditions, a shortage of time, or enough budget you can go to a specialist. |
Summary
Photobiomodulation is a non-invasive and no-pain method with proven efficiency in treating many conditions. Cold laser therapy is not a total scam, however, you should understand the purpose and possible limitations of the treatment.
At-home devices are good options for treating chronic or mild conditions. Many cheap devices use LEDs instead of a laser, which makes them suitable only for treating superficial issues.
Cold laser therapy is a safe procedure with limited contraindications and risks. Pregnant women and people with cancer or blood disease should avoid this treatment. During the procedure, you should always wear protective goggles to avoid eye damage.
FAQ
👀 How long does it take to see results?
Depending on your case, you might see the results immediately after the first session. However, to get constat results 6 to 12 at-office sessions are required. If we speak about at-home devices then you should consult with a provider about duration or follow the instructions.
⏰ How often can I use low laser therapy?
It all depends on the device and the doctor’s recommendations. For example, some instructions say that the device should be used every day for 2 weeks or every other week for 3-4 weeks. Other devices require 2-3 treatments every day.
😏 What is the difference between cold laser therapy and red light therapy?
The main difference is that red light therapy uses only wavelengths in the visible light spectrum. Cold laser therapy also utilizes near-infrared lightwaves which go deeper into tissue.
Sources
- Mechanisms o low level laser therapy. Michael R. Hambling http://photobiology.info/Hamblin.html
- Clijsen R, Brunner A, Barbero M, Clarys P, Taeymans J. Effects of low-level laser therapy on pain in patients with musculoskeletal disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2017;53(4):603-610. doi:10.23736/S1973-9087.17.04432-X
- Barolet D, Roberge CJ, Auger FA, Boucher A, Germain L. Regulation of skin collagen metabolism in vitro using a pulsed 660 nm LED light source: clinical correlation with a single-blinded study. J Invest Dermatol. 2009;129(12):2751-2759. doi:10.1038/jid.2009.186
- Schindl A, Neumann R. Low-intensity laser therapy is an effective treatment for recurrent herpes simplex infection. Results from a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled study. J Invest Dermatol. 1999;113(2):221-223. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1747.1999.00684.x
- Aziz-Jalali MH, Tabaie SM, Djavid GE. Comparison of Red and Infrared Low-level Laser Therapy in the Treatment of Acne Vulgaris. Indian J Dermatol. 2012;57(2):128-130. doi:10.4103/0019-5154.94283
- Suh, D.H. (2007). Red Light Phototherapy Alone Is Effective for Acne Vulgaris: Randomized, Single‐Blinded Clinical Trial. Dermatologic Surgery, 33, 1228–1233.
- Yu HS, Wu CS, Yu CL, Kao YH, Chiou MH. Helium-neon laser irradiation stimulates migration and proliferation in melanocytes and induces repigmentation in segmental-type vitiligo. J Invest Dermatol. 2003;120(1):56-64. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1747.2003.12011.x
- Vaghardoost R, Momeni M, Kazemikhoo N, et al. Effect of low-level laser therapy on the healing process of donor site in patients with grade 3 burn ulcer after skin graft surgery (a randomized clinical trial). Lasers Med Sci. 2018;33(3):603-607. doi:10.1007/s10103-017-2430-4
- Hopkins JT, McLoda TA, Seegmiller JG, David Baxter G. Low-Level Laser Therapy Facilitates Superficial Wound Healing in Humans: A Triple-Blind, Sham-Controlled Study. J Athl Train. 2004;39(3):223-229.
- Lundeberg T, Malm M. Low-power HeNe laser treatment of venous leg ulcers. Ann Plast Surg. 1991;27(6):537-539. doi:10.1097/00000637-199112000-0000
- Schindl A, Heinze G, Schindl M, Pernerstorfer-Schön H, Schindl L. Systemic effects of low-intensity laser irradiation on skin microcirculation in patients with diabetic microangiopathy. Microvasc Res. 2002;64(2):240-246. doi:10.1006/mvre.2002.2429
- Egger A, Resnik SR, Aickara D, et al. Examining the Safety and Efficacy of Low-Level Laser Therapy for Male and Female Pattern Hair Loss: A Review of the Literature. Skin Appendage Disord. 2020;6(5):259-267. doi:10.1159/000509001
- Suchonwanit P, Chalermroj N, Khunkhet S. Low-level laser therapy for the treatment of androgenetic alopecia in Thai men and women: a 24-week, randomized, double-blind, sham device-controlled trial. Lasers Med Sci. 2019;34(6):1107-1114. doi:10.1007/s10103-018-02699-9
- Avci P, Gupta A, Sadasivam M, et al. Low-level laser (light) therapy (LLLT) in skin: stimulating, healing, restoring. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2013;32(1):41-52.